Using SSH Keys with GitHub
Introduction
SSH keys are a secure way to authenticate with GitHub, and they are recommended over using passwords.
Setting them up is very easy but not something I always remember how to do off hand, so this post is here mostly to remind myself of the steps needed!
As with most of my development tools, this process is written with Ubuntu on WSL in mind, but the steps should be similar for other operating systems.
Step 1: Generate a new SSH key
First, we need to generate a new SSH key called id_rsa in the local user .ssh directory. This is done with the following command:
cd ~/.ssh/
ssh-keygen -t rsa -b 4096 -C "<GitHub Email Address>"
If you wish to create different keys for different GitHub accounts or other services, you can add a filename using the -f flag:
cd ~/.ssh/
ssh-keygen -t rsa -b 4096 -C "<GitHub Email Address>" -f id_rsa_<GitHub Username>
Make sure the SSH agent is running using the following command:
eval "$(ssh-agent -s)"
Add the key to your local keystore:
ssh-add ~/.ssh/id_rsa
If you receive the error: Permissions 0755 for '/root/.ssh/id_rsa.pub' are too open, then you simply need to use chmod to change the permissions:
chmod 600 ~/.ssh/id_rsa
Now you can add the public key to GitHub by copying the text from the key file:
cat ~/.ssh/id_rsa.pub
Copy the key text to the clipboard, being careful not to include any whitespace at the beginning or end of the key.
Step 2: Add the SSH key to GitHub
Navigate to the SSH and GPG keys section of your GitHub account settings:
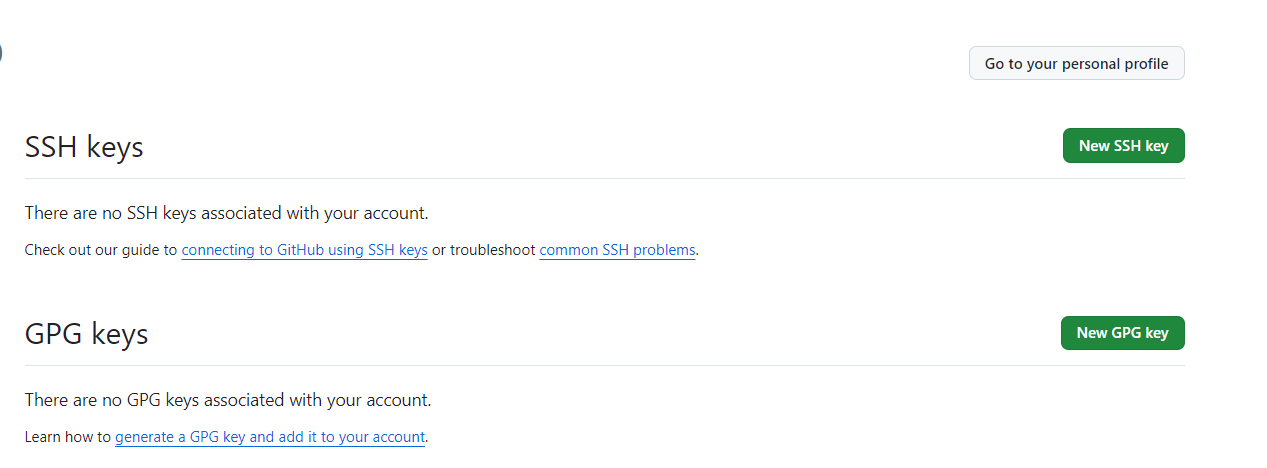
Click “New SSH Key”:
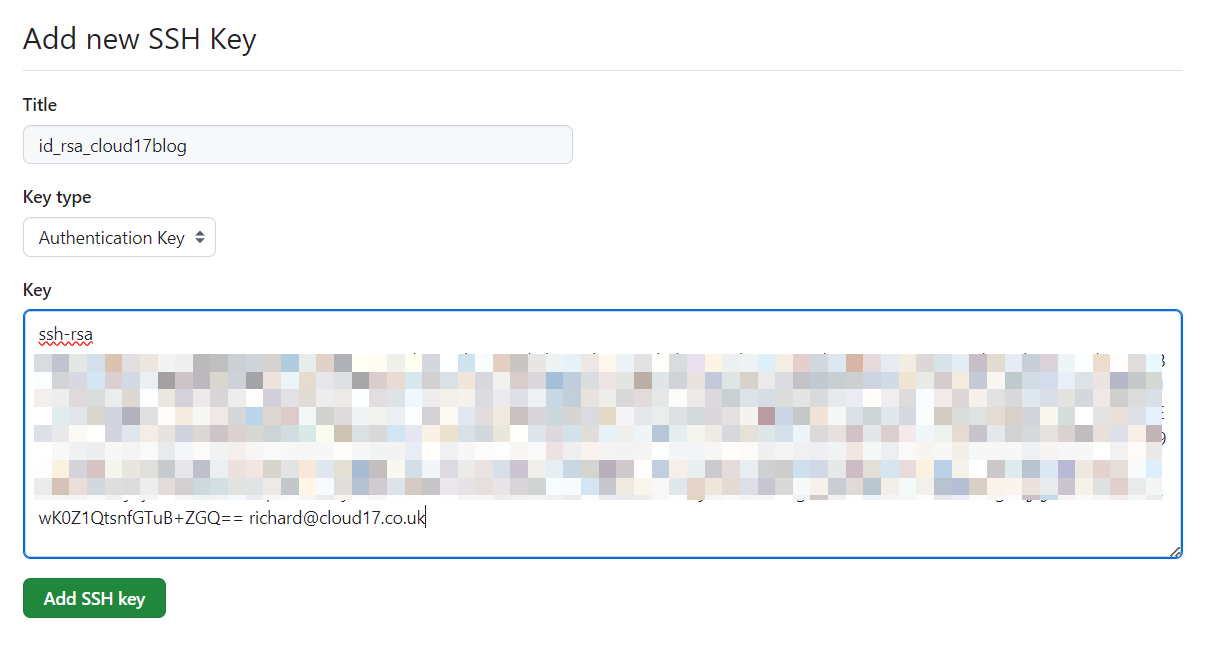
Give the key a title and paste the key text into the “Key” field:
Finally, you can test your SSH connection to GitHub:
ssh -T git@github.com
If everything is set up correctly, you should see a message confirming that you’ve successfully authenticated.
If you were previously using HTTP to access a GitHub repository, you may need to update the remote URL in your Git repositories to use the SSH URL:
git remote set-url origin git@github.com:<username>/<repository>.git
With SSH authentication set up, you can securely interact with your GitHub repositories without needing to enter your username and password each time.